| Alterative |
An agent that gradually restores healthy bodily functions.
|
| Alternative |
Same as alterative. |
| Amenorrhea |
Absence of menstruation. |
| Anther |
The pollen-production portion of the stamen. |
| Anodyne |
An agent that allays or kills pain. |
| Antiscorbutic |
A remedy for scurvy. |
| Appressed |
Lying flat or close against something. |
| Astringent |
An agent producing contraction of tissue or arrest of discharge. |
| Aromatherapy |
Using odors to heal. |
| Avatar |
The embodiment of a deity. |
| Bradycardia |
Abnormally slow heart rate. |
| Bronchus |
One of the main branches of the trachea. |
| Calyx |
The sepals, collectively. |
| Carminative |
A medicine that promotes expulsion of intestinal gas. |
| Catarrh |
Inflammation of a mucous membrane. |
| Cathartic |
An agent producing watery evacuations; a purgative. |
| Corolla |
The petals, collectively. |
| Cordate |
Heart-shaped base.
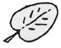
cordate
|
| Corymb |
A flat-topped, open inflorescense.
| simple corymb |
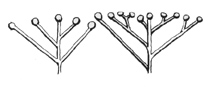 |
compound corymb |
|
| Cuneate |
Wedge-shaped, triangular. |
| Cyme |
A flower cluster in which the central or terminal flower blooms first.
|
| Decoction |
An infusion made in boiling water. |
| Demulcent |
A mucilaginous substance allaying irritation. |
| Depressant |
Having the effect of decreasing vital activity. |
| Depurant |
A cleansing, purifying agent or drug. |
| Diaphoretic |
An agent producing perspiration. |
| Dysmenorrhea |
Pain during menstruation. |
| Emetic |
Agent used to bring on vomiting. |
| Emmenagogue |
Agent stimulating menstrual flow. |
| Emollient |
Agent that softens tissues. |
| Epidermis |
Outer layer of cells. |
| Essential oil |
Natural oil as opposed to synthetic oil. |
| Expectorant |
Agent that promotes the secretion of bronchial mucus |
| Filament |
The stalk of the anther portion of the stamen.
|
| Fomentation |
The application of warm liquids to the body. |
| Glandular |
Bearing glands (secreting agents). |
| Glandular hairs |
Hairs bearing a welling at the tip.
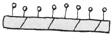
glandular hairs
|
| Globose |
Shaped like a globe or a sphere. |
| Gravel |
Sandlike deposit in the urine. |
| Hallucinogen |
Having the psychoactive effects of producing imaginary perceptions. |
| Inflorescence |
A flower cluster. |
| Infusion |
Liquid prepared by steeping or soaking a drug in water. |
| Involucre |
A whorl of leaves beneath a flower or inflorescence. |
| Lax |
Loose. |
| Lanceolate |
Lance-shaped, several times longer than wide; broadest toward the base.

lanceolate leaf
|
| Leucorrhea |
Inflammation of the vaginal or uterine mucosa, usually characterized by
a whitish or yellowish vagional discharge. |
| Lenticel |
A group of loose corky cells formed beneath the epidermis of woody plants,
rupturing the epidermis and admitting gases to and from the inner tissues.
|
| Mucous membrane |
The thin lining of those cavities and canals communicating with the air. |
| Mucus |
The viscid secretion of mucous membrane. |
| Oblanceolate |
Opposite of lanceolate---broadest toward the tip.

oblanceolate leaf
|
| Oblong |
Two to four times longer than wide; the sides are parallel.

oblong leaf
|
| Obovate |
Inversely egg-shaped; attached at the narrow end.

obovate leaf
|
| Ovate |
Egg-shaped.

ovate leaf
|
| Panicle |
A compound raceme type of inflorescence.
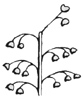
panicle
|
| Pectoral |
A remedy for chest diseases. |
| Petals |
The corolla or inner floral envelope; variously colored.
|
| Petiole |
The stalk of a leaf. |
| Phlegm |
A watery humor; mucus from the bronchi. |
| Pinna |
One of the first divisions of a pinnately compound leaf. |
| Pinnate |
Compound leaf with leaflets on two opposite sides of an elongated axis.
|
odd
pinnate
leaf
|
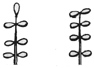 |
even
pinnate
leaf
|
|
| Pinnule |
One of the second divisions of a bi-pinnately compound leaf.
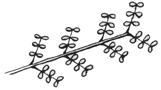
pinnule
|
| Pistil |
The female organ of a flower.
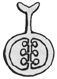
pistil
|
| Pollen |
The male spores. |
| Poultice |
A soft mass, usually moist and heated, spread on a porous cloth and applied
to an inflamed area |
| Psychoactive |
Having an effect on the mind.
|
| Puberulent |
With very short hairs. |
| Pubescent |
Covered with hairs.
puberulent
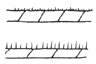
pubescent
|
| Raceme |
An inflorescence with stalked flowers borne on a main axis.
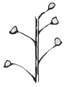
raceme
|
| Rachis |
The central axis of an inflorescence or compound leaf. |
| Rubefacient |
An agent that reddens the skin. |
| Scrofula |
A condition with tumors. |
| Scurvy |
A deficiency disease due to low dietary intake of vitamin C; initial
symptoms include loosening of teeth and damage to the glands.
|
| Sepal |
One of the parts of the outer floral envelope. Usually green. |
| Sepals |
Parts of the calyx, usually green; the outer floral envelope. |
| Serrate |
With sharp teeth directed forward.

|
| Sessile |
Without a stalk. |
| Spike |
An inflorescence with the flowers on a straight axis.

spike
|
| Stamen |
A pollen-bearing organ of a flower made up of anther and filament.
|
stamen
|
 |
anther
filament
|
|
| Stimulant |
Having the effect of increasing vital activity. |
| Stipule |
A modified leaf at the base of a bud. |
| Styptic |
A medicine that causes contraction of the blood vessels and stops bleeding.
|
| Subglobose |
Almost shaped like a globe. |
| Ternate |
Arranged in threes. |
| Tonic |
An agent that produces normal tone or tension. |
| Umbel |
Around or flat-topped inflorescence; the youngest flower is in the center.
simple
umbel |
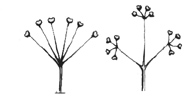 |
compound
umbel |
|
| Vulnerary |
An agent useful in healing wounds. |
![]()

![]()












![]()
